The Gen Z Workforce: Shaping the Future of Work
Related Articles: The Gen Z Workforce: Shaping the Future of Work
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Gen Z Workforce: Shaping the Future of Work. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Gen Z Workforce: Shaping the Future of Work
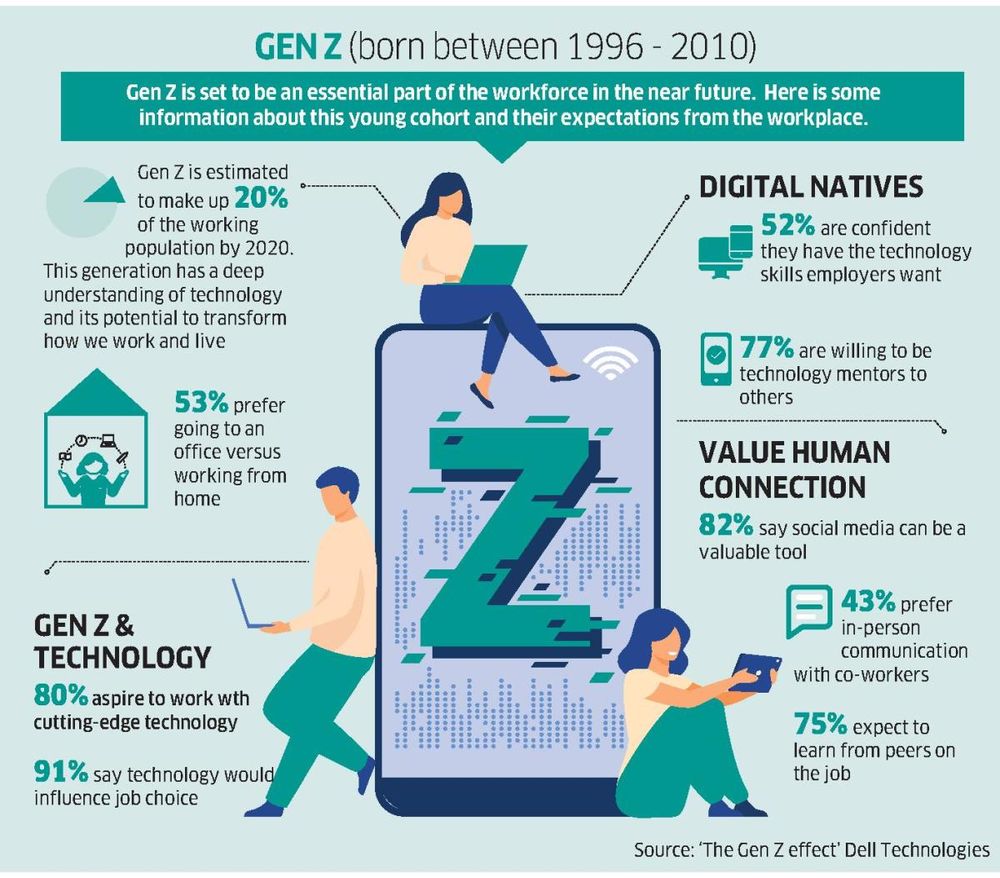
Generation Z, born between 1997 and 2012, is rapidly entering the workforce, bringing with them a unique set of values, skills, and expectations. This generation, shaped by the digital age and globalized world, is redefining the landscape of work, demanding flexibility, purpose, and a strong sense of community from their employers.
This article explores the popular career paths Gen Z is embracing, highlighting the key factors influencing their choices and the implications for the future of work.
The Digital Landscape: Driving Gen Z Career Choices
Gen Z has grown up immersed in technology. Their digital fluency, coupled with a desire for creative expression and problem-solving, has led them to gravitate towards careers in the tech sector.
Software Engineering: The demand for skilled software engineers continues to surge, making it a highly sought-after career path. Gen Z’s innate technological prowess and understanding of coding languages make them well-suited for this field.
Data Science and Analytics: The ability to extract meaningful insights from vast amounts of data is becoming increasingly crucial in a data-driven world. Gen Z’s analytical skills and comfort with data visualization tools position them well for careers in data science and analytics.
Cybersecurity: The rise of cyber threats has created a significant need for cybersecurity professionals. Gen Z’s understanding of digital security and their ability to adapt to evolving threats make them highly valuable in this field.
Digital Marketing: The digital marketing landscape is constantly evolving, requiring professionals with a keen understanding of online platforms, social media, and content creation. Gen Z’s digital fluency and creative flair make them ideal candidates for careers in digital marketing.
Beyond Tech: Diversifying Career Paths
While the tech sector holds strong appeal for Gen Z, their career aspirations extend beyond the digital realm. They are increasingly drawn to fields that offer a sense of purpose and a positive impact on the world.
Healthcare: The aging population and increasing demand for healthcare services have created a robust job market in the healthcare sector. Gen Z’s focus on wellness and their desire to make a difference make healthcare careers appealing.
Sustainability and Environmental Science: Environmental concerns are top of mind for Gen Z, leading them to seek careers in sustainability and environmental science. This sector offers opportunities to address climate change, promote renewable energy, and protect the planet.
Social Work and Education: Gen Z’s commitment to social justice and equality drives their interest in careers in social work and education. These fields allow them to advocate for marginalized communities and contribute to building a more equitable society.
Entrepreneurship: The entrepreneurial spirit is alive and well in Gen Z. Driven by a desire for autonomy and innovation, many are starting their own businesses, leveraging their digital skills and entrepreneurial drive.
Key Factors Shaping Gen Z Career Choices
Several factors influence Gen Z’s career choices, shaping their priorities and aspirations:
- Work-Life Balance: Gen Z prioritizes a healthy work-life balance, seeking flexible work arrangements and opportunities to pursue personal interests outside of work.
- Meaningful Work: Gen Z desires careers that align with their values and make a positive impact on the world.
- Company Culture: A strong company culture that fosters inclusivity, diversity, and collaboration is essential for attracting and retaining Gen Z talent.
- Learning and Development: Gen Z values continuous learning and development opportunities, seeking employers who invest in their growth and provide pathways for career advancement.
FAQs by Popular Jobs for Gen Z
Software Engineering:
- What skills are essential for a software engineer? Proficiency in programming languages like Python, Java, and C++, problem-solving skills, and the ability to work in a collaborative environment.
- What are the educational requirements for a software engineering career? A bachelor’s degree in computer science, software engineering, or a related field is typically required.
Data Science and Analytics:
- What are the key skills needed for a data scientist? Strong analytical skills, proficiency in statistical software like R and Python, data visualization skills, and the ability to communicate insights effectively.
- What are the educational requirements for a data science career? A bachelor’s degree in statistics, mathematics, computer science, or a related field is generally required.
Cybersecurity:
- What are the essential skills for a cybersecurity professional? Understanding of network security, ethical hacking techniques, knowledge of cybersecurity frameworks, and the ability to respond to security incidents.
- What are the educational requirements for a cybersecurity career? A bachelor’s degree in computer science, cybersecurity, or a related field is typically required.
Digital Marketing:
- What skills are essential for a digital marketer? Proficiency in social media platforms, content creation, SEO optimization, online advertising, and data analytics.
- What are the educational requirements for a digital marketing career? A bachelor’s degree in marketing, communications, or a related field is often preferred.
Healthcare:
- What are the different career paths available in healthcare? Nurses, doctors, pharmacists, physical therapists, medical assistants, and healthcare administrators are just some of the many career options within the healthcare sector.
- What are the educational requirements for a healthcare career? Educational requirements vary depending on the specific healthcare profession. Most require a bachelor’s degree or higher.
Sustainability and Environmental Science:
- What are the different career paths available in sustainability and environmental science? Environmental consultants, sustainability managers, renewable energy engineers, and environmental policy analysts are just a few examples.
- What are the educational requirements for a career in sustainability and environmental science? A bachelor’s degree in environmental science, biology, chemistry, or a related field is often required.
Social Work and Education:
- What are the different career paths available in social work and education? Social workers, teachers, counselors, and educational administrators are among the many career options in these fields.
- What are the educational requirements for a career in social work and education? A bachelor’s degree in social work or education is typically required.
Entrepreneurship:
- What skills are essential for an entrepreneur? Entrepreneurs need a strong business acumen, creativity, problem-solving skills, resilience, and the ability to adapt to change.
- What resources are available to support entrepreneurs? Numerous resources, including business incubators, accelerators, and government programs, provide support and guidance to entrepreneurs.
Tips by Popular Jobs for Gen Z
Software Engineering:
- Develop a strong foundation in programming languages: Focus on learning popular languages like Python, Java, and C++.
- Build a portfolio of projects: Showcase your skills and creativity by developing personal projects and contributing to open-source projects.
- Network with other developers: Attend industry events, join online communities, and connect with professionals in the field.
Data Science and Analytics:
- Develop your analytical skills: Practice data analysis techniques, statistical modeling, and data visualization.
- Gain experience with data analysis tools: Become proficient in tools like R, Python, and SQL.
- Develop strong communication skills: Learn to effectively communicate data insights to non-technical audiences.
Cybersecurity:
- Obtain relevant certifications: Pursuing certifications like Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) or CompTIA Security+ can enhance your credibility and job prospects.
- Stay updated on emerging threats: Continuously learn about new cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
- Practice ethical hacking: Develop your skills by participating in ethical hacking competitions and challenges.
Digital Marketing:
- Develop a strong understanding of digital platforms: Become proficient in social media marketing, search engine optimization (SEO), and online advertising.
- Build a portfolio of digital marketing projects: Showcase your skills by creating digital marketing campaigns and analyzing their performance.
- Stay up-to-date with industry trends: Follow industry blogs, attend webinars, and participate in online communities to stay informed about the latest developments in digital marketing.
Healthcare:
- Gain clinical experience through internships and volunteering: Exposure to real-world healthcare settings can help you gain valuable skills and make informed career decisions.
- Develop strong communication and interpersonal skills: Healthcare professionals need to effectively communicate with patients, families, and colleagues.
- Pursue continuing education and professional development: The healthcare field is constantly evolving, so staying up-to-date with the latest advancements is crucial.
Sustainability and Environmental Science:
- Develop a strong understanding of environmental issues: Stay informed about climate change, pollution, and other environmental challenges.
- Gain experience in environmental fieldwork: Participate in research projects, volunteer with environmental organizations, or pursue internships in environmental science.
- Network with professionals in the field: Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and connect with environmental scientists and sustainability experts.
Social Work and Education:
- Gain experience working with vulnerable populations: Volunteer with community organizations, participate in service-learning programs, or intern in social work agencies.
- Develop strong communication and interpersonal skills: Social workers and educators need to effectively communicate with clients, students, and families.
- Pursue advanced degrees: A master’s degree in social work or education can enhance your career prospects and open up opportunities for leadership roles.
Entrepreneurship:
- Develop a strong business plan: Outline your business idea, target market, revenue model, and competitive advantage.
- Network with other entrepreneurs and mentors: Connect with experienced business owners and mentors who can provide guidance and support.
- Explore funding opportunities: Research grants, loans, and angel investors to secure funding for your startup.
Conclusion
Gen Z is entering the workforce with a unique set of values, skills, and expectations. Their digital fluency, desire for purpose, and commitment to social justice are shaping their career choices and redefining the landscape of work. By embracing the values and skills of Gen Z, employers can create a more inclusive, innovative, and sustainable future of work. As Gen Z continues to shape the workforce, their influence will continue to evolve and reshape the way we work, learn, and live.







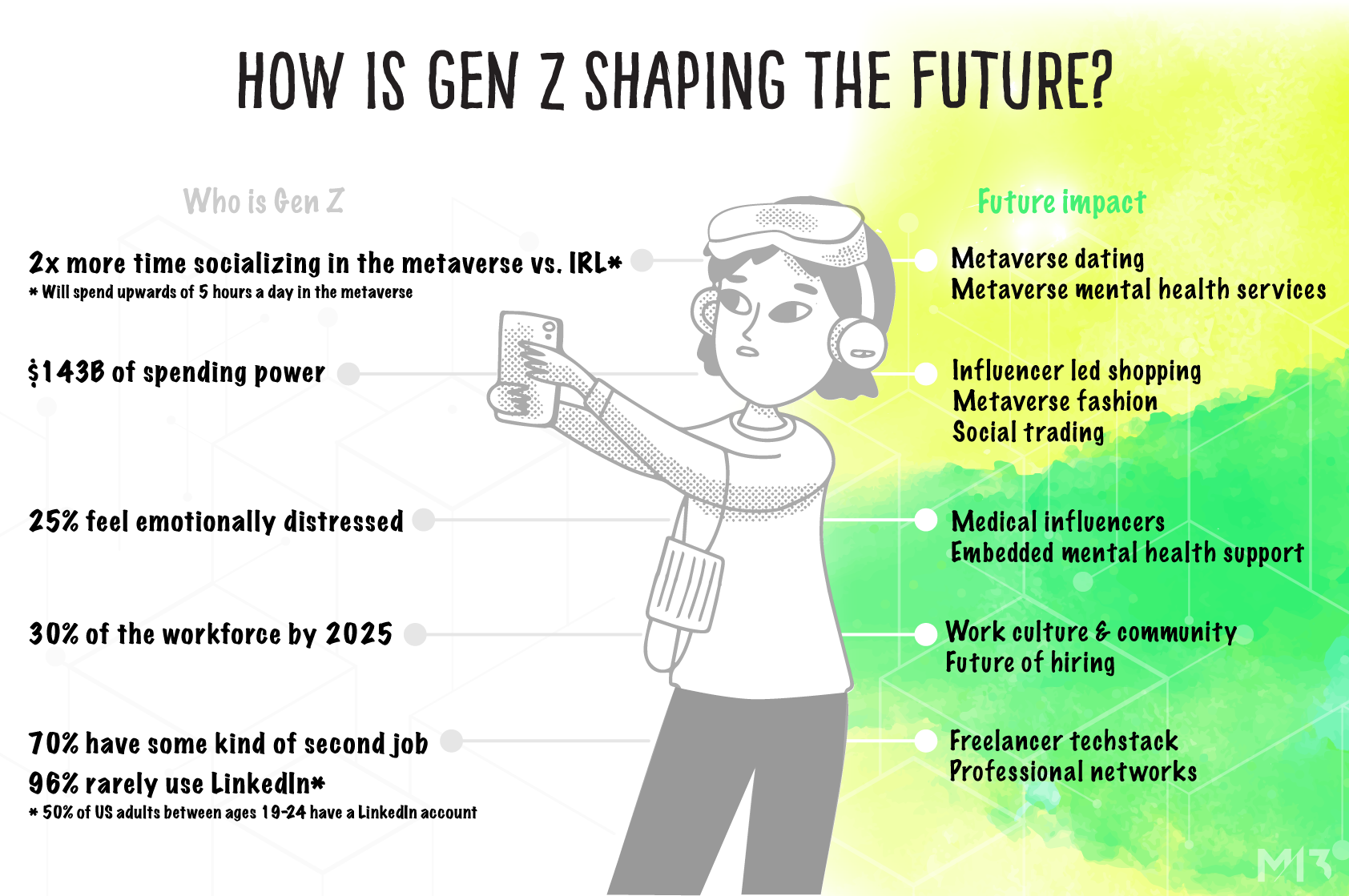
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Gen Z Workforce: Shaping the Future of Work. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!